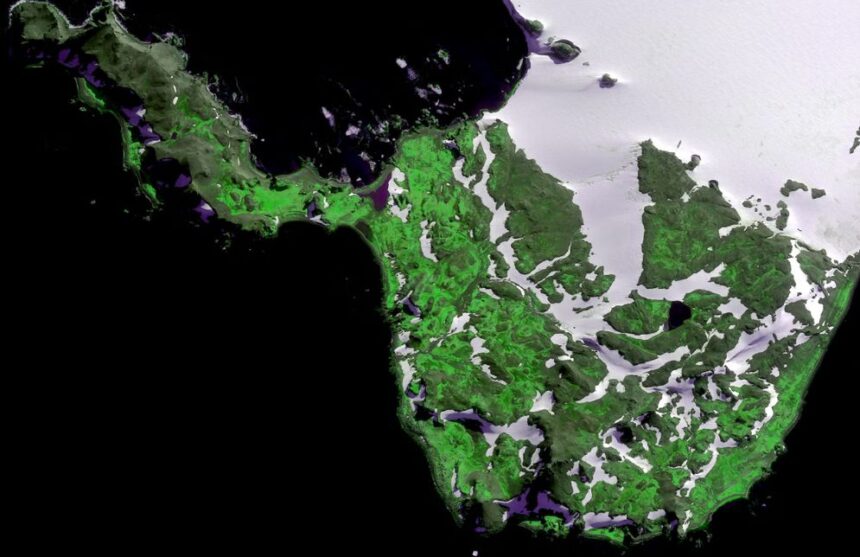
Scientists revealed a startling discovery: Antarctica is turning green! This phenomenon, driven by extreme heat events, is causing rapid plant growth on the icy continent. While greenery is often seen as a positive sign, in Antarctica, it signals a threat to the fragile ecosystem.
Rapid Vegetation Growth
The Antarctic Peninsula, a mountainous region extending toward South America, has been warming significantly faster than the global average. This rapid warming has led to a tenfold increase in vegetation cover over the past four decades. In 1986, vegetation covered less than 0.4 square miles of the peninsula, but by 2021, it had expanded to nearly 5 square miles.
This greening trend is alarming because it disrupts the delicate balance of Antarctica’s ecosystem. The increase in plant life is a direct result of extreme heat events caused by climate change. These events are not only melting ice but also creating conditions favorable for plant growth. As more vegetation takes root, it could further accelerate the warming process, leading to even more ice melt and vegetation growth—a dangerous feedback loop.
Impact on Native Species
The consequences of this greening are far-reaching. The Antarctic Peninsula is home to unique species that have adapted to its harsh, icy environment. The introduction of new plant life could disrupt these species’ habitats and food sources, leading to a decline in biodiversity. Additionally, the melting ice contributes to rising sea levels, which pose a threat to coastal communities around the world.
Scientists from the universities of Exeter and Hertfordshire, along with the British Antarctic Survey, conducted a study to analyze this greening trend. Using satellite data, they found that the rate of vegetation growth has surged by 30% between 2016 and 2021. This rapid increase coincides with a significant decrease in sea ice extent during the same period.
This study highlights the urgent need for action to mitigate climate change and protect Antarctica’s fragile ecosystem. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing conservation measures are crucial steps in preserving this unique and vital part of our planet. International cooperation and policy changes are needed to address the root causes of climate change and prevent further damage.

Global Implications
The greening of Antarctica also has implications for the global climate system. As more vegetation grows on the continent, it will absorb more sunlight, leading to further warming. This process, known as albedo effect, is particularly concerning in polar regions where ice and snow usually reflect sunlight. The loss of ice and snow cover exacerbates this effect, creating a positive feedback loop that accelerates global warming.
Furthermore, the introduction of non-native plant species to Antarctica can have unforeseen consequences. These species could outcompete native plants and disrupt the ecological balance. The fragile Antarctic ecosystem is not equipped to handle such changes, and the impacts could be devastating for its unique flora and fauna.
In addition to environmental concerns, the greening of Antarctica raises geopolitical issues. The Antarctic Treaty System, which governs the use of the continent, was established to preserve its scientific and environmental value. As climate change alters the landscape, the treaty will need to adapt to new challenges. Nations with interests in Antarctica must work together to ensure that the continent remains protected and its ecosystems preserved.
Importance of Public awareness and Education
Public awareness and education are also crucial in addressing the challenges posed by the greening of Antarctica. People around the world need to understand the impact of climate change on the continent and the broader implications for the global climate system. By raising awareness and promoting sustainable practices, we can contribute to efforts to combat climate change and protect Antarctica.
The greening of Antarctica is a stark reminder of the far-reaching effects of climate change. While the increase in plant life may seem like a positive development, it poses a significant threat to the continent’s delicate ecosystem. As we continue to witness the effects of extreme heat events, it is essential to take action to protect Antarctica and ensure the survival of its unique species.
The future of this icy continent depends on our efforts to combat climate change and preserve its natural beauty. The international community must work together to implement effective policies and conservation measures. The role of scientific research in understanding and addressing these issues cannot be overstated. By supporting and funding research, we can gain valuable insights into the impacts of climate change and develop strategies to mitigate its effects.