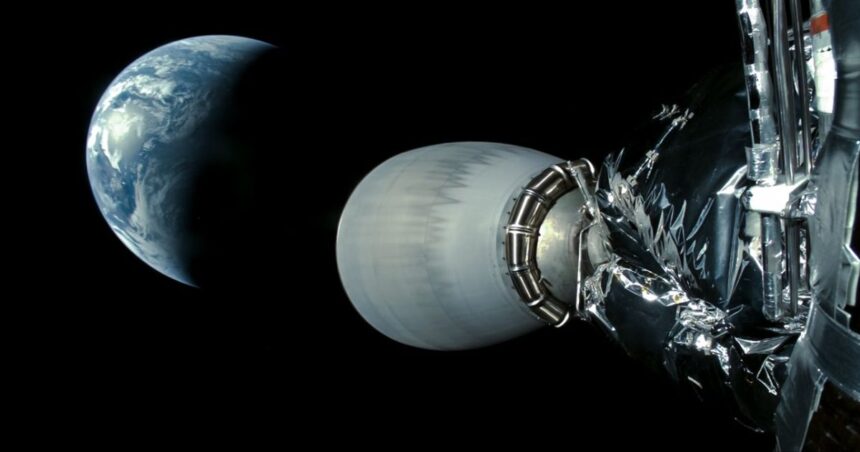
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket captured breathtaking views of Earth while launching the European Space Agency’s Hera asteroid probe. This mission is designed to study the aftermath of NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) on the asteroid Dimorphos. The insights gained from this mission could be pivotal in developing strategies to protect our planet from potential asteroid impacts.
The Falcon 9 rocket lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at precisely 10:52 a.m. EDT. As the rocket ascended into space, its onboard camera captured a series of remarkable images showcasing our beautiful planet against the dark backdrop of space.
Earth Views from Space
One of the standout images shows Earth as a small, vibrant blue sphere framed by the Falcon 9’s upper stage and the nozzle of its Merlin engine. These images provide a humbling reminder of our planet’s fragility and the vastness of space.
Shortly after liftoff, approximately 76 minutes into the flight, the Hera spacecraft separated from the Falcon 9’s upper stage, marking the beginning of its journey to the binary asteroid system Didymos.
Deployment of @ESA’s Hera confirmed pic.twitter.com/E1QiekBSB3
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) October 7, 2024Hera’s primary mission is to study the changes caused by NASA’s DART mission, which deliberately crashed into Dimorphos, a small moonlet orbiting the larger Didymos, in a bid to test a planetary defense technique. This impact, intended to alter Dimorphos’s trajectory, simulates how we might deflect an asteroid on a collision course with Earth.
Hera’s mission will provide a detailed examination of the DART impact site, gathering data on the crater and the material ejected during the collision. This information will help scientists understand the dynamics of asteroid impacts and refine their models for asteroid deflection.
By closely analyzing Dimorphos, Hera aims to validate the effectiveness of the kinetic impactor technique as a viable method for planetary defense.
The Hera mission is vital for planetary defense research. It aims to gather comprehensive data on the consequences of asteroid impacts, which is crucial for developing strategies to protect Earth from future threats.
By understanding the mechanics of asteroid deflection, scientists can better prepare for potential asteroid collisions that could pose significant risks to our planet.
The successful launch of Hera was achieved despite challenging weather conditions. The mission team closely monitored the weather and made precise calculations to ensure a safe and successful liftoff.
The successful separation of Hera from the Falcon 9 rocket was confirmed when the spacecraft made contact with ground control shortly after deployment. This initial success sets a positive tone for the mission as Hera embarks on its two-year journey to the Didymos system.
View from Falcon 9's second stage during the Hera mission pic.twitter.com/a4Qrgg6Pp6
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) October 7, 2024Upon reaching the Didymos system in 2026, Hera will deploy two CubeSats, flying close to Dimorphos to take high-resolution images and collect additional data.
These CubeSats will complement Hera’s observations, comprehensively understanding the impact’s effects and the asteroid’s characteristics. The data collected by Hera and its CubeSats will be invaluable for future planetary defense missions and our understanding of asteroid systems.
The images captured by the Falcon 9 rocket during the Hera launch serve as a powerful reminder of Earth’s beauty and the importance of space exploration.
These images not only inspire wonder but also highlight the significance of missions like Hera in safeguarding our planet. The mission exemplifies international collaboration in space exploration, with agencies like ESA and NASA working together to achieve common goals.
The successful launch and deployment of Hera are just the beginning of what promises to be an exciting and groundbreaking mission. As Hera travels through space, scientists eagerly await the wealth of data it will provide.
This information will enhance our understanding of asteroids and the effectiveness of asteroid deflection techniques, ultimately contributing to the safety and security of our planet.